
Yesterday a massive DDoS attack targeted the DNS service of the Dyn company, one of the most authoritative domain name system (DNS) provider, and caused an extended Internet outage. A large portion of Internet users was not able to reach most important web services, many websites like including Twitter, GitHub, PayPal, Amazon, Reddit, Netflix, and Spotify were down for netizens in the US.
What happened? Who his behind the attack?
The fear of cyber attack on a global scale brought people in the panic, yesterday a large portion of users have probably understood that the Internet architecture is a resource that could be targeted by hackers with serious and unpredictable consequences.
But how the attack happened? What’s the cause behind the attack?
We still ignore the exact dynamic of the attack, neither who is the responsible, the unique certainty is that the Dyn DNS Service was flooded by a devastating wave of requests originated by million of compromised IoT devices. The Dyn company reported a huge army of hijacked Internet of Things devices could be abused by attackers to power the massive DDoS attack.
The security intelligence firm Flashpoint published an interesting post on the massive DDoS in which confirm that its experts have observed the Mirai bots driving the attack against DynDNS.
“Flashpoint has confirmed that some of the infrastructure responsible for the distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against Dyn DNS were botnets compromised by Mirai malware. Mirai botnets were previously used in DDoS attacks against security researcher Brian Krebs’ blog “Krebs On Security” and French internet service and hosting provider OVH.” reads the analysis published by Flashpoint “Mirai malware targets Internet of Things (IoT) devices like routers, digital video records (DVRs), and webcams/security cameras, enslaving vast numbers of these devices into a botnet, which is then used to conduct DDoS attacks. “
Below the Key Findings of the report published by Flashpoint
This is not surprising if we consider that the source code of the botnet was leaked of the popular criminal hacker forum Hackforum earlier October by a user with moniker “Anna-senpai” that shared the link to the source code of the malware “Mirai.”
“The leak of the source code was announced Friday on the English-language hacking community Hackforums. The malware, dubbed ‘Mirai’ spreads to vulnerable devices by continuously scanning the Internet for IoT systems protected by factory default or hard-coded usernames and passwords.” reported Krebs.

The Mirai Botnet was first spotted by the researcher MalwareMustDie this summer targeting IoT devices, it mainly targets connected objects such as routers, CCTV, and DVRs.
The Mirai malware target Internet of Things (IoT) devices using the credential factory settings, a circumstance that is quite common in the wild.
The availability of the source code of Mirai Botnet in the wild theoretically made possible everyone to power a botnet.
I confess you that I believe the leak of the source code of such kind of botnet could be also part of a wider strategy of a certain category of attackers that intend to power massive attacks making impossible the attribution.
Watch out! The Mirai botnet that powered the attack against the Dyn DNS service is not the same used against Krebs’s site and OVH.
“While Flashpoint has confirmed that Mirai botnets were used in the October 21, 2016 attack against Dyn, they were separate and distinct botnets from those used to execute the DDoS attacks against “Krebs on Security” and OVH. Earlier this month, “Anna_Senpai,” the hacker operating the large Mirai botnet used in the Krebs DDoS, released Mira’s source code online.” continues Flashpoint “Since this release, copycat hackers have used the malware to create botnets of their own in order to launch DDoS attacks.”
It is unknown if the attacks against Dyn DNS are linked to the DDoS attacks against Krebs, OVH, or other previous attacks.
The attack against a DNS aims to obtain a wide effect, in the specific case many sites and services are using Syn as their upstream DNS provider.
If you are interested to know more about the diffusion of the Mirai Botnet you can use this online tracker that reports more than 1.2 Million IPs seen associated to devices infected by the Mirai code in the wild. Consider that isn’t the exact number of infected devices, because many of them use dynamic IPs.
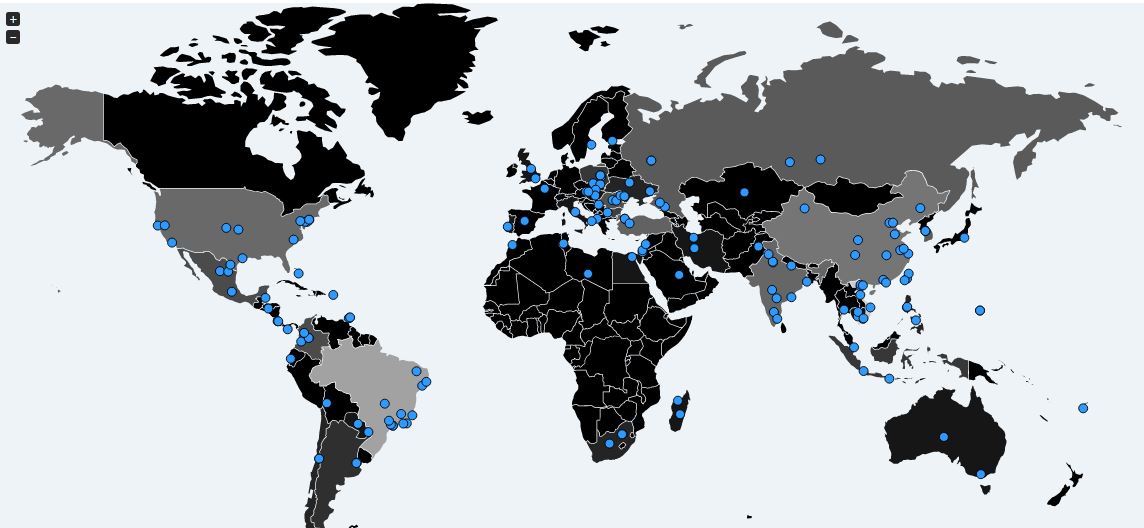
According to the Reuters, the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and the FBI are both investigating the massive DDoS attacks against the Dyn DNS service.
We have no indication about the possible culprit, I personally believe that the leakage of the Mirai botnet in the wild and this last massive attack have something in common and there is a specific strategy of a persistent attacker behind the events.
| [adrotate banner=”9″] | [adrotate banner=”12″] |
(Security Affairs – Dyn DNS service, massive DDoS)
[adrotate banner=”5″]
[adrotate banner=”13″]