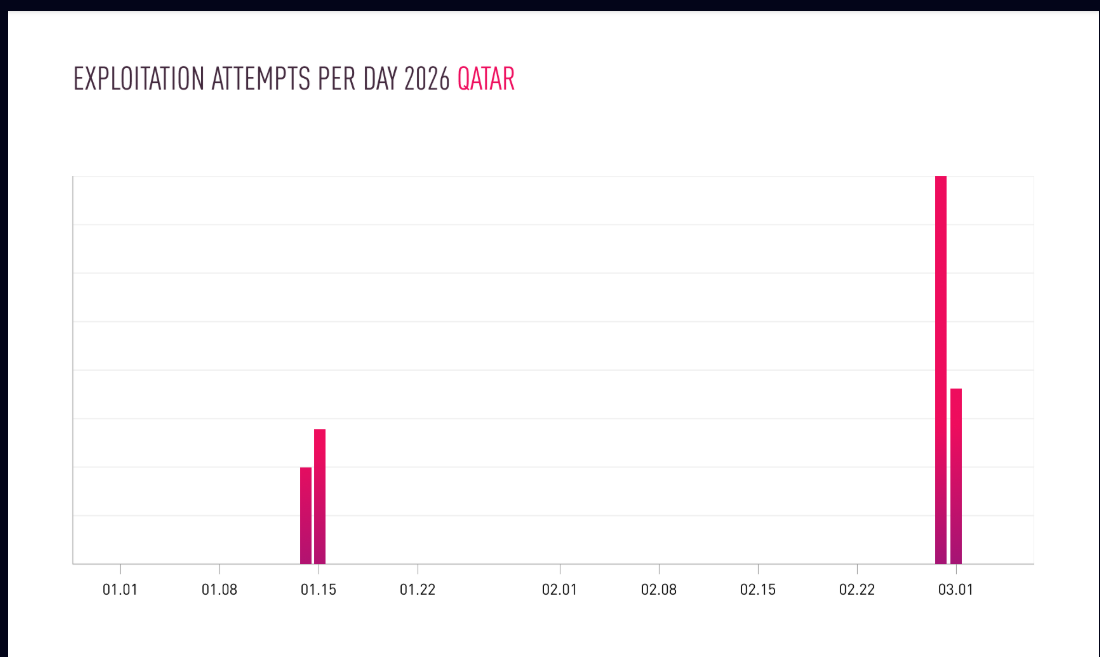
Former NSA hacker, demonstrated how to subvert the Kaspersky Lab antivirus and turn it into a powerful search tool for classified documents.
The Kaspersky case demonstrated that security software can be exploited by intelligence agencies as a powerful spy tool.
Patrick Wardle, chief research officer at Digita Security and former NSA hacker, demonstrated it by subverting the Kaspersky Lab antivirus and turning it into a powerful search tool for classified documents.
“In the battle against malicious code, antivirus products are a staple,” Patrick Wardle told the New York Times. “Ironically, though, these products share many characteristics with the advanced cyberespionage collection implants they seek to detect.”