
Uptycs’ threat research team has discovered a new Botnet named ‘Simps’ attributed to Keksec group primarily focussed on DDOS activities. We discovered the Simps Botnet binaries downloaded via shell script sample and Remote Code Execution vulnerability exploits by Gafgyt – detailed in our earlier post.
Based on our analysis and threat intelligence, we have the following observations:
This post will cover details on our discovery, threat intelligence data attributing relations to Keksec group, working of the binaries and the code similarity, and reuse modules of Simps Botnet.
Discovery of Simps Botnet
During the first week of May 2021, the Uptycs’ threat research team detected a shell script and Gafgyt malware downloading Simps binaries from the same C2- 23.95.80[.]200.
Shell script downloading Simps binary
The shell script (hash: c2d5e54544742b7a1b04cf45047859a10bb90c6945d340120872f575aa866e6d), ‘ur0a.sh’ was downloaded from the C2 URL 23.95.80[.]200.
The script downloaded several next stage payloads for several *nix architectures from the open directory named “Simps” in the same C2 URL from where the shell script was downloaded (see Figure 1)

Figure 1: Malicious Shell script dropping payloads
The script performs the following:
On execution of the Simps binary, it drops a log file containing that the device has been infected with malware by Simps Botnet (see Figure 2)

Figure 2: Dropped log file
The binary also connects to the C2 23.95.80[.]200 (see figure 3)

Figure 3: C2 communication
Gafgyt downloading Simps binary
During this same time, Gafgyt binary (hash: e847dfbd831df6015519d03d42ada8241ce1174e9bd96f405452627617229c63) was also downloading Simps binary from the same C2 URL. The Simps payload was delivered by exploiting multiple Remote Code Execution vulnerabilities in vulnerable IOT devices. An excerpt of Realtek and Linksys router exploits downloading the next stage payloads. (see Figure 4 and 5)

Figure 4: Linksys router exploit

Figure 5: Realtek router exploit
Both these exploits downloaded a Simps MIPS UPX packed binary (hash – 6d18b433183fc68cd7b731fed198732d3460a21afba53163f059152bd410b55f), for MIPS architecture which also displays a message that the device has been infected by Simps Botnet (see Figure 6)

Figure 6: Simps ELF execution
Simps Botnet – Youtube channel and Discord server
While looking into the historical data of our threat intelligence systems and passive DNS records, we identified several malicious URLs (hash in IOCs section below) downloading a shell script named ur0a.sh and containing Simps next stage payloads. Another commonality was the Simps Botnet infection log message. Searching for these common entries led us to a YouTube video titled “Simps Botnet😈, Slamming!!!”, created by a user named “itz UR0A” created on 24 April 2021. (see Figure 7)

Figure 7: Youtube video demo of Simps Botnet
The Youtube link also contained a Discord server link of “UR0A”, which was also present in the infection log. (see Figure 8)

Figure 8: Simps Botnet Discord server
Keksec attribution with Simps Botnet
The Discord server contained several discussions around DDOS activities and Botnets carrying different names. One binary we identified in a chat conversation named gay.x86 (hash: e258a284d5cad584a14df27f022c99515de1cec69ab3157640d1ce7584c50ecd). Upon execution, it displayed a message that the system is pawned by md5hashguy (see Figure 9)

Figure 9: Discord message
We also came across another Gafgyt malware from a Joesandbox report, that contained the Infected By Simps Botnet 😉 message. This malware dropped a file name “keksec.infected.you.log” that contained a message “youve been infected by urmommy, thanks for joining keksec..” (see Figure 10)

Figure 10: keksec.infected.you.log file
Interestingly, the same Discord server also contained an users named “urmommy” and “698a20e0da24bcebca57f09b7d695f8d#2881” who actively involved in DDOS activities and Botnet discussions. All this data gathered tied reactions Simps Botnet and the Discord server users related to Keksec group. This group is also referred as Kek Security, which according to NSFOCUS is a group which operates HybridMQ-keksec, a Botnet created with Trojan programs. HybridMQ-keksec is a DDoS Trojan program obtained by combining and modifying the source code of Mirai and Gafgyt.”
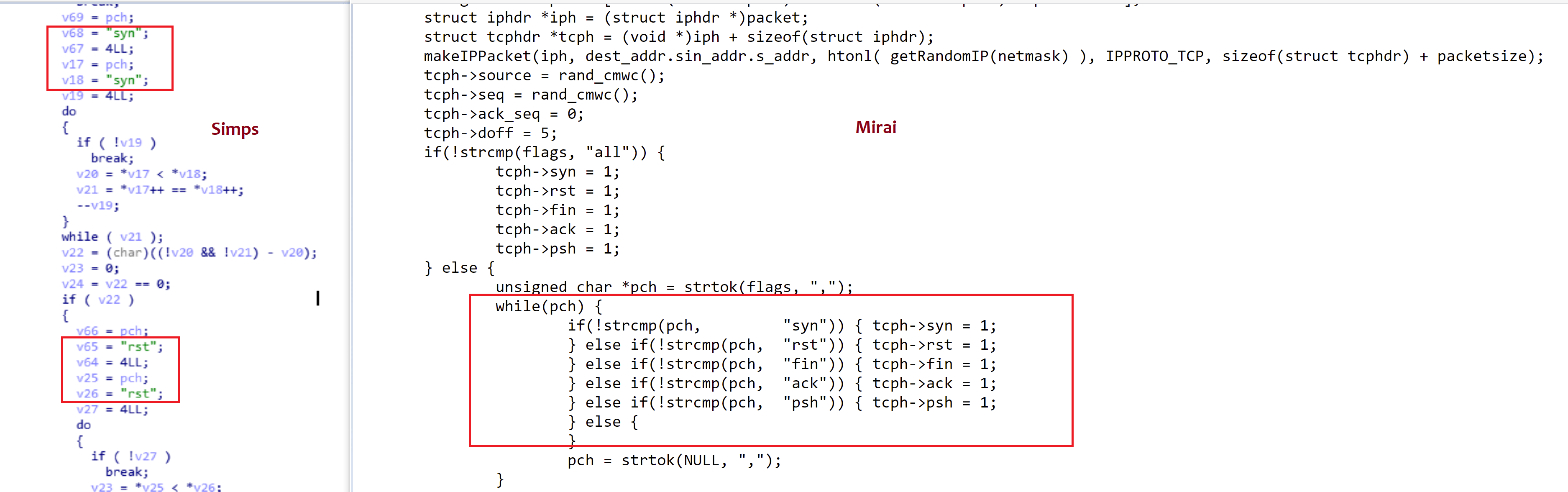
Figure 11: TCP flood module of Simps and Mirai

Figure 12: UDP flood module of Simps and Mirai
Similarly, Simps binaries also have the Valve source Engine and OVH modules which were also seen in a variant of Gafgyt that targeted Huawei and Asus Routers and killed its rival IoT Botnets. The code similarity of the Valve source Engine module used by Simps was similar to Gafgyt. (see Figure 13)

Figure 13: VSE attack module of Simps and Gafgyt
Uptycs EDR Detections
Uptycs’ EDR capabilities, armed with YARA process scanning, detected Simps downloader shell-script activity (See Figure 13) and the Simps ELF binary with a threat score of 10/10 (See Figure 14).

Figure 14: Shell script detection

Figure 15: Simps binary detection
Additionally, Uptycs’ EDR also detects the outbound connection of the malware C2 URLs via our threat intelligence.
Conclusion
Our research initially started with the discovery and analysis of Simps Botnet binaries used for DDOS activities. Using Uptycs’ EDR, threat intelligence data and Open-source intelligence (OSINT) we were able to tie relations and attribute Simps Botnet to the Keksec group. The Uptycs threat research team has reported the associated Discord server, Youtube and Github links to the concerned entities. We will continue to monitor the developments of this group and share updates.
Additional details, including Indicators of Compromise are available in the original post available at the following URL:
https://www.uptycs.com/blog/discovery-of-simps-botnet-leads-ties-to-keksec-group
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook
| [adrotate banner=”9″] | [adrotate banner=”12″] |
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, Simps Botnet)
[adrotate banner=”5″]
[adrotate banner=”13″]